Metal Sputtering Target Materials and Their Uses
Sputtering is a core physical vapor deposition (PVD) technique used to deposit thin films for industrial such as electronics, optics, and photovoltaics. In this process, energetic ions bombard the surface of a source material, releasing atoms that subsequently form a thin film coating.
Many different types of source materials, or sputtering targets, are used depending on the film to be deposited. Particularly, one common type of sputtering target includes pure metal targets.
1. Pure Metal Targets
1.1. About Metal Sputtering Targets
A metal sputtering target (not to be confused with alloy sputtering targets) is made out of elemental metals. These types of targets are available in high purity grades, such as 99.999% purities, ensuring minimal contamination in thin film coating applications.
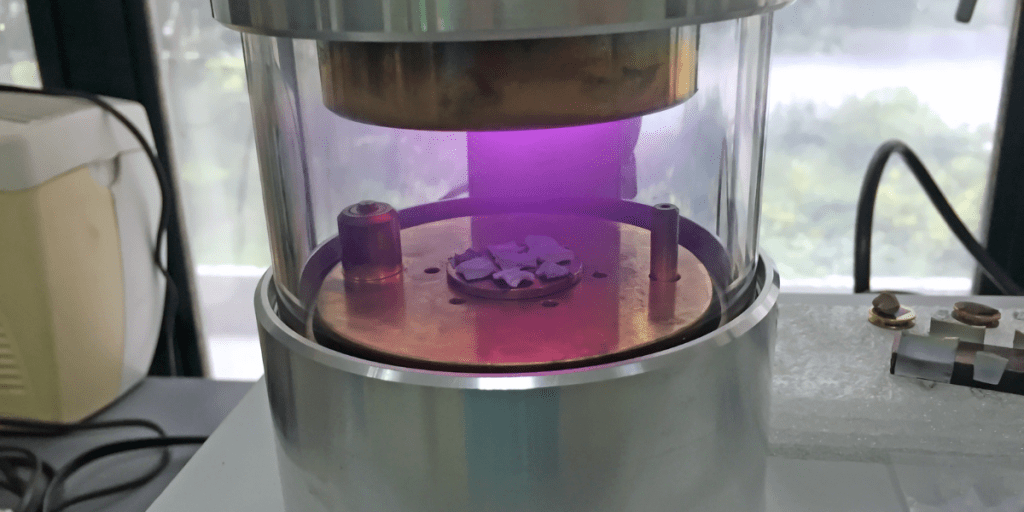
Image: sputter coater process in a lab
Thin film metals exhibit a wide range of properties, and specific metals are selected for precise coating depositions due to their high electrical conductivity in electronic applications, reflective properties for optical devices, or mechanical strength for wear resistance.
2. Metal Sputtering Target Examples
2.1. Chromium Targets
Chromium (Cr) is known for excellent corrosion resistance and hardness. These coatings form a protective layer that resist oxidation, making them ideal for increasing wear resistance.
Industries often use chromium sputtering targets in automotive and aerospace components to enhance part durability. Chromium also serves as an intermediate layer between thin film coatings due to its strong adhesion properties.
2.2. Copper Targets
Copper (Cu) exhibits high thermal and electrical conductivity. Industries such as the semiconductor industry widely use it to create interconnects and circuitry on integrated circuits (ICs) and printed circuit boards (PCBs).
2.3. Gold Targets
Gold (Au) shows good electrical conductivity and optical properties, demonstrating reflectivity in visible and infrared spectra. Thin films of gold are used in many applications: e.g. electrical contacts, reflective layers, and widely used for decorative finishes.
2.4. Iron Targets
Iron (Fe) is fundamental for the deposition of ferromagnetic thin films. Coatings can be used in magnetic sensors and electronics, co-deposited to form iron-based alloys for magnetic layers in data storage devices,
2.5. Tantalum Targets
Tantalum (Ta) is a refractory metal demonstrating a high melting point and excellent conductivity. This material is also highly resistant to corrosion and has low vapor pressure, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Tantalum sputtering targets find use in the electronics industry, used for thin films that act as diffusion layers, preventing copper diffusion from occurring.
2.6. Tungsten Targets
Tungsten (W) exhibits an extremely high melting point, excellent mechanical strength, and low vapor pressure. Applications that require resistance to high temperatures and wear often employ tungsten thin films.
Electrical applications use tungsten thin films as a conductive material that does not wear out from electric arcs, such as for interconnects.
Sourcing Sputtering Targets
R.D. Mathis Company provides target materials known for their high purity, creating reliable performance for thin film coating processes. For more information about specialty materials, contact us for a quote.