Compounds for Sputtering Targets in Thin Film Deposition
Sputtering targets are high purity evaporation materials that enable the deposition of thin films through a process of ejecting atoms via ion bombardment. For many applications, specific compound sputtering targets are chosen to fabricate uniform thin films with calibrated properties.
1. Sputtering Target Materials
1.1. Introduction
Materials used in sputtering targets range from metal targets (elemental and alloy), semiconductors, ceramics, or targets made of composite materials. The wide range of depositable thin film materials enables sputter deposition to see use in diverse applications, ranging from industrial tool coatings to novel materials research.
2. Compound Sputtering Targets
Compound sputtering targets are source materials that combine multiple elements in a specific stochiometric ratio. For instance, metal oxides are a common substance that tend to be used in optics for their refractive index. Depending on the composition, compounds can produce thin films with many different properties, such as:
2.1. Oxide Sputtering Targets
As stated previously, oxides see use in optical applications for tuning optical properties. This group of materials also shows a range of electrical properties, being used as either insulators in some cases or conductors in others.
Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) is one example of the aforementioned oxide sputtering targets, often combined with glass substrates. ITO combines optical transparency with electrical conductivity, making it widely used for coatings in electronic displays, touchscreens, and solar panels.
2.2. Fluoride Sputtering Targets
Fluoride targets are heavily utilized as transparent coatings with anti-reflective properties for laser and sensor films. These can also serve as scratch resistant coatings when deposited onto lenses or mirrors in optical systems.
Magnesium fluoride (MgF2) is transparent material across a range of different wavelengths. As a result, high-powered laser components use MgF2 films to enhance light transmission and minimize interference from reflections.
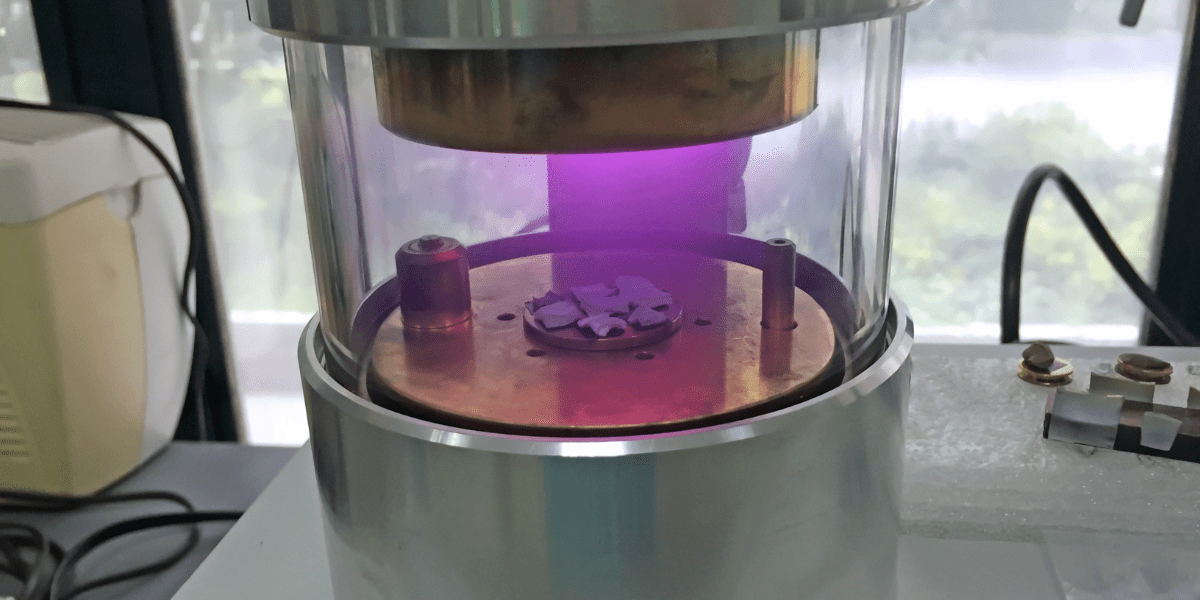
Image: sputter coater process in a lab
2.3. Carbide and Nitride Sputtering Targets
Numerous wear-resistant coatings use both carbide and nitride thin film materials. Many metalworking cutting tools use titanium nitride or tungsten carbide as a hard protective layer due to how they performance under mechanical stress and high temperature conditions.
3. Other Compound Sputtering Targets
3.1. Sulfide, Selenide, and Telluride Sputtering Targets
Other types of compound sputtering targets include sulfides, selenides, tellurides, seeing use in optoelectronics and solar cells. A broad spectrum of compound materials can be explored for thin‑film applications, and ongoing research into novel compounds allows further engineering of film properties, for advanced functionalities.
Overall, thin film compounds exhibit a diverse range of properties that enable their use in numerous optical, electronic, and functional applications, tailored to meet specific performance requirements.
Sourcing Thin Film Deposition Materials
R.D. Mathis Company manufactures materials that support advances in thin film deposition. Specializing in high-quality production, our team can provide compound sputtering targets tailored to specific application requirements upon request.
View standard selections for elemental targets, or contact us for specialized sputtering targets.