Common Types of Evaporation Sources
Evaporation sources serve as critical components used in physical vapor deposition (PVD), a technique used to deposit thin films of material onto a substrate.
Standard boat sources, resistive heating elements that hold material, encompass a large selection of evaporation sources and are made from molybdenum, tantalum, and tungsten sheet. Filament sources, constructed from tungsten wire, also constitute another major class of evaporation sources.
The geometry of these filaments is tailored to specific applications to achieve desired thermal and deposition characteristics. The following section provides an overview of three commonly employed source types.
About Filament Sources
Before discussing particular types of filament sources, it is important to know about how filament sources work. As a material, tungsten is an ideal for evaporation baskets because it has a high melting point (3422°C), a low vapor pressure and is relatively inert in a vacuum environment.
Evaporation material is added onto a filament source by wrapping material in the form of wire on top. Material can also come in the form of clips or canes, which hang onto the filament. During deposition, this material sticks onto the tungsten wire due to wetting when the evaporation material is molten.
What is the purpose of multi-stranded wire?
Stranded wire (e.g. 3x.025W, 3 strands of 0.025″ diameter tungsten wire) increases the surface area that material can wet to. This increases the holding capacity of tungsten filament sources
1. Tungsten Evaporation Baskets
Tungsten evaporation baskets consist of a basket-shaped container made of tungsten wire, which is heated to a high temperature through resistive heating. Design of the basket shape allows for the material to be evenly distributed when evaporating, which helps to ensure a uniform deposition onto the substrate.
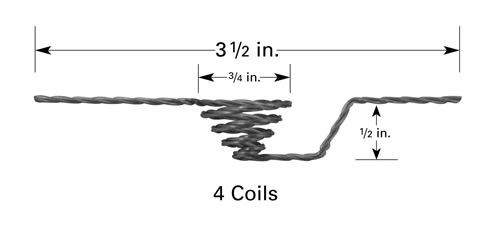
Filaments can be instead shaped into tungsten basket heaters, which hold crucibles rather than directly hold material on the wire. By doing so, the crucible can be heated with low power requirements when compared to other methods of crucible heating.
2. Point Source Filaments
Point source filaments evaporate the material from a small point on the filament, hence resulting in a highly directional vapor flow that can be used to deposit material in a precise and controlled manner. This is advantageous for applications where accuracy at small scales is required, such as the production of micro-electronic devices or optical components.
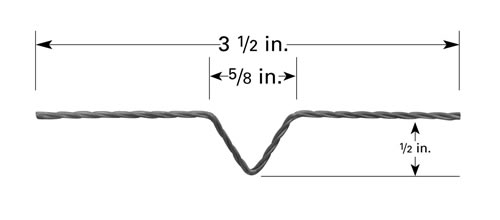
Overall, point source filaments are a useful tool for vacuum deposition processes that require a high degree of precision and control. They are commonly used in the production of a wide range of products, including semiconductors, optical coatings and thin films for scientific research.
3. Alumina Coated Evaporation Sources
Alumina-coated sources are covered with a ceramic layer. This alumina (Al2O3) coating provides several benefits to the evaporation source. It offers a protective layer that helps to prevent the bare metal from reacting with the material being deposited. Both boat sources and filament sources can be coated with alumina.
Notably, the alumina coating on a basket (RDM-WBAO) forms what is essentially an internal heated crucible. With the tungsten filament embedded between the alumina, it provides an effective way to evaporate corrosive materials such as gold.
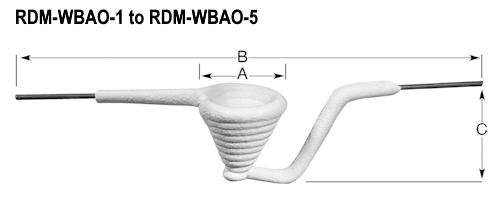
The alumina also provides good thermal properties, which helps maintain stable temperatures in the crucible during the deposition process. This helps to promote uniform deposition of the material being deposited.
RD Mathis Company’s Evaporation Sources
RD Mathis Company specializes in the design, manufacturing and distribution of high-quality vacuum components and thin film deposition equipment. Our technical support and consulting services has helped many customers optimize their vacuum processes and achieve their goals.
Custom design and manufacturing services to meet specific customer requirements are available. Contact us for more information or view all of our evaporation sources.